
” Depression is a war you fight alone, but don’t have to win by yourself.” – Unknown.
Depression is a mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities once enjoyed. It can affect daily functioning and overall quality of life. Symptoms may include:
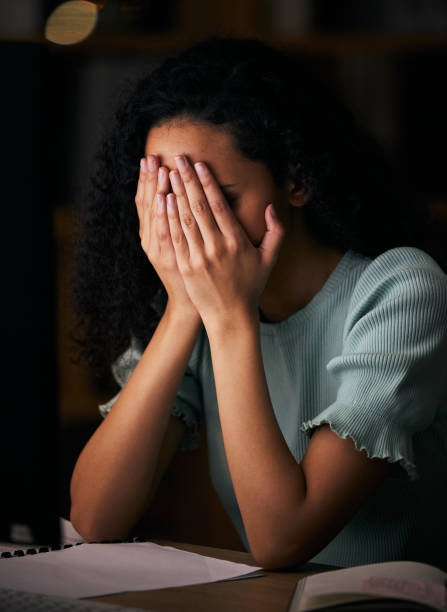
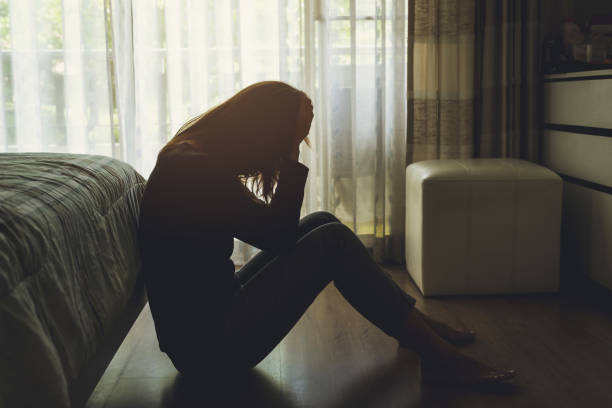


What to Expect in Therapy for Depression:

We integrate several evidence-based approaches to provide comprehensive support. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective treatments for depression, helping you recognize and challenge harmful thought patterns and guiding you toward healthier alternatives.
Behavioral Activation (BA) is also a key approach, helping you reintroduce meaningful activities into your life. Often, depression leads to disengagement from activities, and BA focuses on increasing positive, rewarding behaviors to improve mood and energy levels.
Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) focuses on improving interpersonal relationships and communication skills, addressing social issues that may be contributing to depression. By enhancing your connections with others, IPT can help reduce feelings of isolation and improve emotional support. Additionally, we may incorporate Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), which encourages accepting difficult emotions while committing to actions aligned with your values. Mindfulness-based approaches help you develop awareness of the present moment, reducing the impact of negative thoughts and emotions.
Therapy for depression is an opportunity for healing. Together, we’ll work to restore hope, build emotional resilience, and help you lead a more fulfilling life.

Welcome to Psychology and Beyond, LLC. Our core values include a celebration of diversity, a strength-based approach, and connectedness.
Seamlessly visualize quality intellectual capital without superior collaboration and idea sharing listically
© 2022 • Psychology and Beyond, LLC
Design and Developed by Algor Labs brand of Split Arts